Translations and Textual Transmission
Posted on
In this episode, Peter Adamson of King's College London introduces the podcast as a whole, and the thought of the early Greek philosophers called the Presocratics. He also discusses the first Presocratic philosopher, Thales of Miletus.
Posted on
Peter introduces philosophy in late antiquity, when Aristotelianism and Platonism made a comeback, and pagan philosophy developed alongside Judaism and Christianity.
Posted on
Peter looks at the history of Aristotelianism up the time of the Roman Empire and the beginning of commentaries on Aristotle's works.
Posted on
Sir Richard Sorabji, founder of the Ancient Commentators Project, joins Peter to discuss the history of ancient commentary on Aristotle.
Posted on
Boethius ushers in the medieval age with expert works on Aristotle, subtle treatises on theology, and the Consolation of Philosophy, written while he awaited execution.
Posted on
Greek philosophy and science make their way into the Islamic world via Syriac and Arabic translations and interpretations.
Posted on
Miskawayh, al-‘Āmirī, al-Tawḥīdī, the Brethren of Purity and Ismā'īlī missionaries bring together philosophy with Persian culture, literature and Islam.
Posted on
A special 150th double interview episode on the transmission of philosophy from Arabic into Latin.
Posted on
Robert Wisnovsky joins Peter to discuss the enormous body of unstudied philosophical commentaries in the later Eastern Islamic world.
Posted on
Philosophy in Safavid Iran, and a look back at earlier philosophy among Shiites.
Posted on
Sajjad Rizvi talks to Peter about Mullā Ṣadrā's views on eternity, God's knowledge and the afterlife.
Posted on
Alcuin leads a resurgence of interest in philosophy and the liberal arts at the court of Charlemagne.
Posted on
Stephen Gersh (who was Peter's doctoral advisor!) joins him to discuss the sources and influence of Platonism in the Middle Ages.
Posted on
Little-known authors prepare the way for scholasticism with glosses on logic, metaphysical debate, and a poem about a cat.
Posted on
Greek and Arabic sources are rendered into Latin in a translation movement that will revolutionize medieval philosophy.
Posted on
Rival philosophical schools proliferate and subdivide in our second major historical period, the “age of the sūtra.”
Posted on
An introduction to philosophical developments in Buddhism and Jainism up to the time of Dignāga in the sixth century AD.
Posted on
An interview with Monica Green reveals parallels between medicine and philosophy in the middle ages.
Posted on
Did Indian ideas play a role in shaping ancient Greek philosophy?
Posted on
The impact of ancient Indian thought upon the Muslim scholar al-Bīrūnī and upon European thinkers like Hume, Hegel, and Schopenhauer.
Posted on
We begin to look at the third tradition of medieval philosophy, in which the heritage of classical antiquity is preserved and debated by the Byzantines.
Posted on
Eastern Christian philosophy outside of Constantinople, focusing on translation and exegesis in the languages of Syriac and Armenian.
Posted on
Translations of religious and philosophical texts into Ge’ez, a national epic called the Kebra Nagast, and other developments in the story of philosophy in Ethiopia.
Posted on
Photius, “the inventor of the book review,” and other Byzantine scholars who preserved ancient learning.
Posted on
Walda Heywat’s reaction to the thought of his teacher Zera Yacob, and the dispute over the authenticity of these two Ethiopian philosophers.
Posted on
The spread of Islamic scholarship in subsaharan Africa, focusing on intellectuals of the Songhay empire around the Niger River in the 15th-17th centuries.
Posted on
Peter speaks to Souleymane Bachir Diagne about Islamic scholars in West Africa.
Posted on
A conversation with Sam Imbo on approaching oral traditions as philosophy and the Ugandan thinker and poet Okot p'Bitek.
Posted on
Katerina Ierodiakonou discusses Byzantine commentators on Aristotle, including Michael of Ephesus.
Posted on
Without handwritten copies produced by Byzantine scribes, we would know almost nothing about ancient philosophy. How and why were they made?
Posted on
Oliver Primavesi tells us how Greek manuscripts are used to establish the text of authors like Aristotle.
Prof Primavesi runs the Munich School of Ancient Philosophy together with Christof Rapp and Peter Adamson.
Posted on
The Neoplatonist Proclus gets mixed reviews from Christians, as Nicholas of Methone refutes him but the Georgian philosopher Ioane Petritsi helps to revive his thought.
Posted on
Intellectual exchange between Christians and Muslims, and the later flowering of Syriac literature including the philosopher Bar Hebraeus.
Posted on
Historian Judith Herrin joins us to talk about competition and mutual influence between Islam and Byzantium.
Posted on
Mathematics and the sciences in Byzantium, focusing on scholars of the Palaiologan period like Blemmydes and Metochites.
Posted on
Thomas Aquinas finds avid readers among Byzantines at the twilight of empire, and is used by both sides of the Hesychast controversy.
Posted on
When the Byzantine empire ended in 1453, philosophy in Greek did not end with it. In this episode we bring the story up to the 20th century.
Posted on
The series on Byzantium concludes as guest Michele Trizio discusses the mutual influence of Byzantium and Latin Christendom.
Posted on
A first look at the themes and figures of philosophy in the Italian Renaissance.
Posted on
Bessarion and George Trapenzuntius, rival scholars from the Greek east who helped inspire the Italian Renaissance.
Posted on
Coluccio Salutati and Leonardo Bruni combine eloquence with philosophy, taking as their model the refined language and republican ideals found in Cicero.
Posted on
Lorenzo Valla launches a furious attack on scholastic philosophy, favoring the resources of classical Latin.
Posted on
Jill Kraye returns to the podcast to discuss the nature of humanism, its relation to scholasticism, and its legacy.
Posted on
The rediscovery of Epicurus, Lucretius, and Sextus Empiricus spreads challenging ideas about chance, atomism, and skepticism.
Posted on
The blossoming of Renaissance Platonism under the Medici, who supported the scholarship of Poliziano, Ficino, and Pico della Mirandola.
Posted on
Marsilio Ficino’s revival of Platonism, with a focus on his proofs for the soul’s immortality in his magnum opus, the Platonic Theology.
Posted on
An interview with Denis Robichaud on how, and why, Plato was read in the Italian Renaissance.
Posted on
Jewish philosophers in Renaissance Italy, focusing on Leone Ebreo’s Dialogues of Love, the Averroism of Elijah del Medigo, and Italian Kabbalah.
Posted on
The blurry line dividing humanism and scholastic university culture in the Italian Renaissance.
Posted on
Aristotle’s works are edited, printed, and translated, leading to new assessments of his thought among both humanists and scholastics.
Posted on
An interview with David Lines on the Renaissance reception of Aristotle's Nicomachean Ethics.
Posted on
An interview with Dag Nikolaus Hasse on the Renaissance reception of Averroes, Avicenna, and other authors who wrote in Arabic.
Posted on
The humanist study of Pythagoras, Archimedes and other ancient mathematicians goes hand in hand with the use of mathematics in painting and architecture.
Posted on
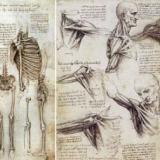
Connections between philosophy and advances in medicine, including the anatomy of Vesalius.
Posted on
The impact of the printing press on the history of philosophy, and its role in helping to trigger the Reformation.
Posted on
Rudolph Agricola, Juan Luis Vives and other humanist scholars spread the study of classical antiquity across Europe and mock the technicalities of scholastic philosophy.
Posted on
The “learned piety” of Desiderius Erasmus, the greatest figure of northern humanism.
Posted on
John Sellars returns to the podcast to discuss Lipsius' work on Seneca and the early modern Neo-Stoic movement.
Posted on
A chat with Ann Blair about the "Theater of Nature" by Jean Bodin, and other encyclopedic works of natural philosophy. (Pictured: Prof Blair holding the annotated copy of Bodin's Theatrum she describes in the episode.)
Posted on
The first leader of independent Tanzania grounds his socialist ideas in traditional African values.
Posted on
Joseph Scaliger, Isaac Casaubon, and Guillaume du Vair grapple with history and the events of their own day.
Posted on
Humanism comes to England and Scotland, leading scholars like Thomas Eylot and Andrew Melville to rethink philosophical education.
Image: Queen Elizabeth's translation of Boethius
Posted on
We're joined by Patrick Gray to discuss Shakespeare's knowledge of philosophy, his ethics, and his influence on such thinkers as Hegel.
Posted on
How one of Kenya's greatest writers came to argue that African literature should be written in African languages.
Posted on
How scientists of the Elizabethan age anticipated the discoveries and methods of the Enlightenment (without necessarily publishing them).
Posted on
An expert on Renaissance alchemy tells us how this art related to philosophy at the time... and how she has tried to reproduce its results!
Posted on
How religious persecution and censorship shaped the context of philosophy in Catholic Europe in the sixteenth century.
Posted on
Iberian expeditions to the Americas inspire scientists, and Matteo Ricci’s religious mission to Asia becomes an encounter between European and Chinese philosophy.
Posted on
Co-host Karyn introduces herself to the listeners and talks about the challenges of tackling classical Chinese philosophical texts.
Posted on
Fray Luis de Leon, Antonio Nebrija, Beatriz Galindo and other scholars bring the Renaissance to Spain.